CPT Transporte Pagado a: El Pasaje Pagado
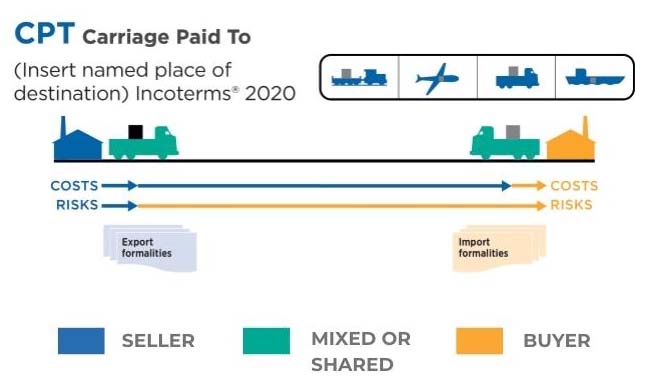
Bajo el término CPT Carriage Paid To, el vendedor paga el transporte hasta el lugar de destino convenido, pero el riesgo se transfiere al comprador una vez que la mercancía ha sido entregada al primer transportista. Imagínese que está en un tren, cómodamente sentado, sabiendo que su billete ha sido pagado. Eso es el CPT. Introducido en 1980, el CPT es un giro moderno del CFR, que refleja el paso del transporte marítimo al multimodal.
Obligaciones del vendedor:
Entregar la mercancía al transportista en el lugar de embarque convenido.
Pagar el coste del transporte hasta el lugar de destino convenido.
Despachar las mercancías para la exportación.
Obligaciones del comprador:
Despachar las mercancías para la importación, pagando los posibles derechos de aduana.
Asumir todos los riesgos de pérdida o daño una vez entregada la mercancía al transportista.
Instancia CPT:
CPT: Transporte pagado hasta
Utilicemos un ejemplo para explicar la tarificación y el envío con el Incoterm CPT (Carriage Paid To).
Podemos utilizar este escenario: Un vendedor chino envía productos electrónicos a un comprador de Estados Unidos.
He aquí cómo se desglosarían los costes:

- Coste del producto: El precio acordado para la electrónica es de $20.000.
- Logística local: Costes de entrega de la mercancía desde el almacén hasta el puerto en China (responsabilidad del vendedor), digamos $1.000.
- Despacho aduanero de exportación: Gastos de despacho de exportación de la mercancía por la aduana china (a cargo del vendedor), digamos $500.
- Gastos de transporte: Coste de envío de la mercancía a través del océano hasta el puerto de destino en EE.UU. (responsabilidad del vendedor según el CPT), digamos $2.000.
Por tanto, el coste total para el vendedor (precio CPT) es de $20.000 + $1.000 + $500 + $2.000 = $23.500.
Envío:
- Despacho aduanero de importación: Aranceles e impuestos de aduanas de EE.UU. (a cargo del comprador), digamos $3.000.
- Logística local: Costes de entrega de la mercancía desde el puerto hasta el almacén del comprador en EE.UU. (a cargo del comprador), digamos $1.000.
Por lo tanto, el coste total para el comprador debería ser el precio CPT ($23.500) más los costes del despacho de aduanas de importación ($3.000), y la logística local ($1.000). Es decir, $23.500 + $3.000 + $1.000 = $27.500.
Según el CPT, el vendedor tiene la obligación de organizar y pagar el transporte de la mercancía hasta el destino convenido, pero el riesgo se transfiere del vendedor al comprador en cuanto la mercancía se entrega al primer transportista, lo que difiere del término FOB.
¿Qué término está cerrado a CPT?
El Incoterm más similar a CPT es PIC (Transporte y seguro pagados hasta). En ambos casos, el vendedor debe organizar y pagar el transporte de la mercancía a un destino determinado. La diferencia clave es que en el CIP, el vendedor también tiene que contratar y pagar un seguro contra el riesgo del comprador de pérdida o daño de la mercancía durante el transporte. En ambos casos, el vendedor tiene que organizar y pagar el transporte, pero sólo en el CIP tiene que organizar también el seguro. En ambos casos, el riesgo de pérdida o daño se transfiere del vendedor al comprador en cuanto la mercancía se entrega al primer transportista.


